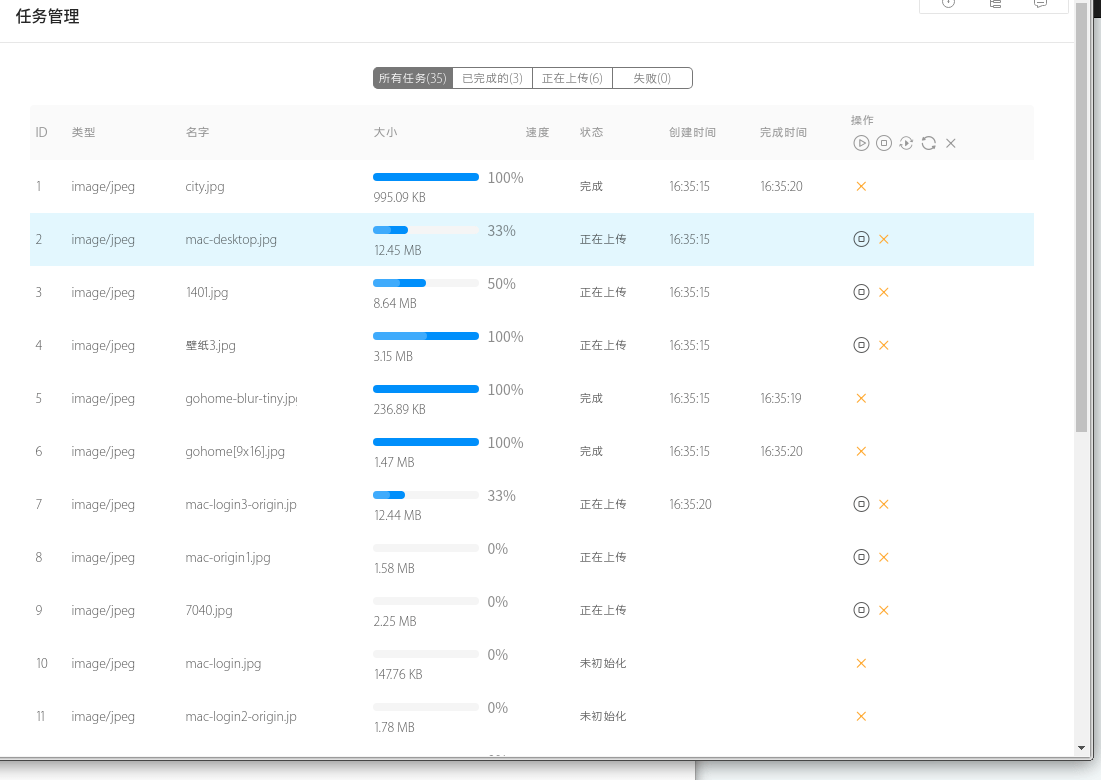
目录 概述
文件上传-Js向中间层Node发送分片数据
文件上传-中间层Node接收前端发送的分片数据
文件下载-中间层Node获取后端文件数据的两种处理
文件下载-Js下载中间层文件的两种不同方式
预览
概述 Amazon S3 提供了一个简单 Web 服务接口,可用于随时在 Web 上的任何位置存储和检索任何数量的数据。此服务让所有开发人员都能访问同一个具备高扩展性、可靠性、安全性和快速价廉的数据存储基础设施, Amazon 用它来运行其全球的网站网络。此服务旨在为开发人员带来最大化的规模效益。基于s3对象存储多文件分片上传的Javascript实现(一) 主要讲了前端Js多文件分片上传逻辑的实现,描述了浏览器端多文件分片异步上传状态管理方面的设计,这篇文章主要针对前端Coder文件操作的一些痛点,比如:前端分片是以怎样的数据形式发送到中间层的、中间层是怎样接收前端发送的分片数据的、文件下载时中间层怎样处理后端接口返回的大文件数据然后发送给前端、前端又是怎样拿到和下载中间层返回的文件数据的,主要包含这些方面。
文件上传-Js向中间层Node发送分片数据 创建Axios实例 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 const XHR = axios.create ({ baseURl : '' , timeout : 30e3 , headers : originHeaders, validateStatus (status ) { return status >= 200 && status < 300 ; }, });
使用文件分片构造表单数据 fileShardsData为File.slice接口对文件截取得到的部分文件数据
1 2 const data = new FormData ();formData.append ('file' , fileShardsData, 'file' );
发送分片 注意设置请求头的请求数据类型
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 XHR ({ api, method, data, headers : { 'Content-Type' : 'multipart/form-data' , }, }).then ((response ) => { ... });
文件上传-中间层Node接收前端发送的分片数据 Express没有自带文件处理功能,需要使用第三方middleware
环境:
编写公用中间处理组件 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 const formidable = require ('formidable' );exports .formidableParseFile = (req, res, callback ) => { try { const form = new formidable.IncomingForm (); form.parse (req, (err, fields, files ) => { if (fs.existsSync (files.file .path )) { fs.readFile (files.file .path , (err, fileBuffer ) => { fs.unlink (files.file .path , (err ) => { if (err) console .log (err); }); if (err) { return callback (err); } callback (null , fileBuffer); }); } else { callback (null , '' ); } }); } catch (error) { console .error (error); callback (error); } }
挂载路由 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 router.post ('/object/object/upload' , function (req, res, next ) { console .log ('upload' ); const random = Math .random (); console .time (`${random} -> 1` ); formidableParseFile (req, res, (err, fileBuffer ) => { console .timeEnd (`${random} -> 1` ); if (err) { return res.json ({ code : 500 , result : err.toString (), }) } console .time (`${random} -> 2` ); commonRequestAuth (req.query , objectsresourceApi.object .uploadObject , req, fileBuffer).then ( (response ) => { console .timeEnd (`${random} -> 2` ); res.json ({ code : response.code , result : { ...{ etag : response.headers ? response.headers .etag : '' }, ...response.result }, }); }, ); }); });
方法2:代码实现文件处理 声明方法 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 exports .parseFile = (req, res, callback ) => { req.setEncoding ('binary' ); let body = '' ; let fileName = '' ; const boundary = req.headers ['content-type' ].split ('; ' )[1 ].replace ('boundary=' , '' ); req.on ('data' , function (chunk ) { body += chunk; }); req.on ('end' , function ( try { const file = querystring.parse (body, '\r\n' , ':' ) const fileInfo = file['Content-Disposition' ].split ('; ' ); for (value in fileInfo) { if (fileInfo[value].indexOf ("filename=" ) != -1 ) { fileName = fileInfo[value].substring (10 , fileInfo[value].length - 1 ); if (fileName.indexOf ('\\' ) != -1 ) { fileName = fileName.substring (fileName.lastIndexOf ('\\' ) + 1 ); } } } const entireData = body.toString (); contentType = file['Content-Type' ].substring (1 ); const upperBoundary = entireData.indexOf (contentType) + contentType.length ; const shorterData = entireData.substring (upperBoundary); const binaryDataAlmost = shorterData.replace (/^\s\s*/ , '' ).replace (/\s\s*$/ , '' ); const binaryData = binaryDataAlmost.substring (0 , binaryDataAlmost.indexOf ('--' + boundary + '--' )); callback (null , binaryData); } catch (error) { callback (new Error ('form-data parse error!' )); } }); };
挂载路由同上 文件下载-中间层Node获取后端文件数据的两种处理 两种方式均使用Axios发送请求
小文件直传 接收到接口数据后直接放入内存然后以文件的类型发送给前端
请求header注意设置resType: "arraybuffer" 1 2 3 4 5 6 router.post ('/resource/object/detailinfo/all' , function (req, res, next ) { commonRequestAuth ({ ...req.body , ...{ $no_timeout$ : true }}, objectsresourceApi.object .objectinfoAll , req).then ((response ) => { res.type ('file' ).send (response.result ) }); });
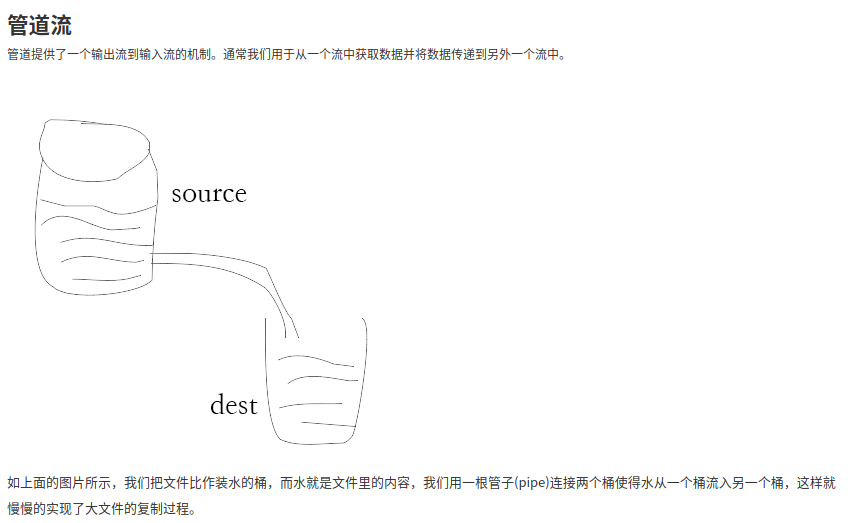
大文件转存为静态资源 Node.js支持文件流操作,包含可读流、可写流以及可读可写流,如果在处理大文件的时候直接把数据放入内存,就会出现中间层内存爆满的情况,这里先声明接口返回数据为可读流,然后通过本地静态资源路径创建可写流,最后为了避免由于可读流的数据写入可写流时由于读取速度和写入速度的差异问题导致的数据丢失情况,使用管道pipe连接可读流和可写流再进行数据传输。
Node Pipe管道的概念
请求header注意设置resType: "stream"
创建本地可写流
接口返回的是可读流,可以直接连接到管道
可写流完成写入后向前端发送静态资源文件地址
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 router.post ('/resource/object/detailinfo' , function (req, res, next ) { console .log ('download' ); commonRequestAuth ({ ...req.body , ...{ $no_timeout$ : true }}, objectsresourceApi.object .objectinfo , req).then ((response ) => { console .log ('download callback' ); const fileName = req.body .object .split ('/' ).pop (); const fileSymbol = `${fileName} -${Date .now()} ` ; const filePath = path.join (_path.public , 'download' , fileSymbol); const ws = fs.createWriteStream (filePath); response.result .pipe (ws); ws.on ('finish' , () => { console .log ('download finish' ); res.header ({ 'Content-Disposition' : fileName }); res.json ({ code : 200 , result : filePath.split ('node-express-react/public/public' )[1 ], }); }); }); });
文件下载-Js下载中间层文件的两种不同方式 小文件直接从接口拿到数据并生成DataURL触发下载 请求header声明responseType:arraybuffer
接口数据返回后生成前端通用的大二进制块数据Blob
使用HTML5 FileReader接口读取二进制块
构造a标签并指名download属性下载DataURL
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 downloadObjectInMemory = (para, info ) => { const iAxios = axios.create (); iAxios.defaults .timeout = 0 ; const options = { method : 'POST' , url : '/resource/object/detailinfo/all' , withCredentials : true , responseType : 'arraybuffer' , headers : { 'Cache-Control' : 'max-age=0' , 'X-Requested-With' : 'XMLHttpRequest' , 'Content-Type' : 'application/json' , 'Access-Control-Allow-Origin' : '*' , }, data : para, }; const readAsDataUrl = (data, emptyData ) => { const reader = new FileReader (); reader.readAsDataURL (data); reader.onload = (e ) => { const url = e.target .result ; const a = document .createElement ('a' ); const filename = para.object .split ('/' ).pop (); a.href = url === 'data:' ? emptyData : url; a.download = filename; a.click (); window .URL .revokeObjectURL (url); }; }; const typename = mapMimeType (info.name ).mime ; iAxios.request (options) .then ((res ) => { const blobData = new Blob ([res.data ], { type : typename }); readAsDataUrl (blobData, `data:${typename} ;base64,` ); }).catch ((error ) => { console .log (error); }); }
大文件通过接口返回的静态文件链接进行下载 步骤同上,只不过构造DataURL的过程取消,a标签可以直接使用接口返回的静态文件地质URL
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 downloadObjectWithURL = (para ) => { const iAxios = axios.create (); iAxios.defaults .timeout = 0 ; const options = { method : 'POST' , url : '/resource/object/detailinfo' , withCredentials : true , responseType : 'json' , headers : { 'Cache-Control' : 'max-age=0' , 'X-Requested-With' : 'XMLHttpRequest' , 'Content-Type' : 'application/json' , 'Access-Control-Allow-Origin' : '*' , }, data : para, }; let timer; iAxios.request (options) .then ((res ) => { clearTimeout (timer); const a = document .createElement ('a' ); const filename = para.object .split ('/' ).pop (); const address = process.env .NODE_ENV === 'development' ? `${window .location.protocol} //10.0.6.206:3000${res.data.result} ` : `${window .location.protocol} //${window .location.hostname} :3000${res.data.result} ` ; a.href = address; a.download = filename; a.click (); }).catch ((error ) => { console .log (error); }); timer = setTimeout (() => { openNotification ('info' , null , this .lang .lang .fileDownloadTips ); }, 1e3 ); }